Professional and high-quality metal alloys, ceramic products and concrete additives | RBOSCHCO
PRODUCT PARAMETERS
Description
Introduction of Boron Carbide Plate
Boron Carbide Plate is a high-performance ceramic plate made from boron carbide (B4C) material. Boron carbide is a super-hard material with high hardness, low density, and excellent wear, and corrosion resistance, and it is widely used in industrial, military, and nuclear energy applications. A boron carbide plate is usually made using a hot press sintering or cold press sintering process, with dense structure and excellent mechanical properties.
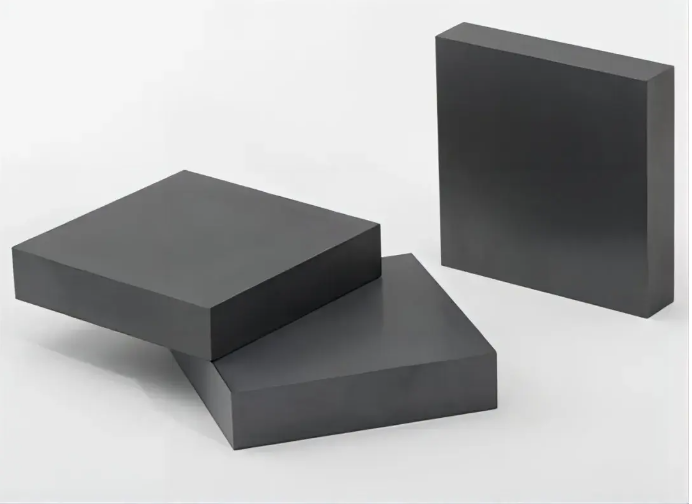

Features of Boron Carbide Plate
High hardness: The hardness of boron carbide is second only to diamond and cubic boron nitride, with Mohs hardness as high as 9.3, making it an ideal wear-resistant material.
Low density: With a density of approximately 2.52 g/cm³, it is lighter than most metals and ceramic materials, making it suitable for lightweight applications.
Excellent Wear Resistance: Boron carbide plates have extremely high wear resistance and are suitable for high-wear environments.
High-Temperature Resistance: With a melting point of up to 2450°C, it maintains stable mechanical properties at high temperatures.
Corrosion resistance: Excellent corrosion resistance to acids, alkalis, and most chemical reagents.
Neutron absorption capacity: Boron carbide has a high absorption cross-section for neutrons and is a commonly used neutron absorption material in nuclear reactors.
High rigidity: It has a high modulus of elasticity and can withstand large mechanical stress.
Parameters of Boron Carbide Plate
| Property | Specification |
| Chemical Formula | B₄C |
| Hardness (Vickers) | ~35 GPa |
| Density | 2.52 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 2450°C (4442°F) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 27-129 W/m·K (depending on purity and orientation) |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 6.5 × 10⁻⁶ K⁻¹ |
| Electrical Resistivity | High (acts as an electrical insulator) |
| Compressive Strength | > 3.5 GPa |
| Tensile Strength | Relatively low due to brittleness |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 460-500 GPa |
| Fracture Toughness | Low (~3 MPa·m^(1/2)) |
| Chemical Stability | Highly resistant to most acids, alkalis, and molten salts |
| Neutron Absorption Cross Section | High (~760 barns for natural boron) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in most environments |
| Acoustic Properties | Good sound damping characteristics |
| Biocompatibility | Generally considered biocompatible |
| Environmental Impact | Non-toxic; long service life reduces replacement frequency |
| Manufacturing Process | Hot pressing, sintering, reaction bonding |
| Typical Applications | Armor plating, abrasive materials, nuclear applications, industrial wear parts |
Applications of Boron Carbide Plate
Bulletproof armor: Used in the manufacture of lightweight bulletproof vests, bulletproof inserts, and vehicle armor, providing high protection performance.
Nuclear industry: used as neutron absorbing materials for control rods and shielding materials in nuclear reactors.
Wear-resistant parts: Used in the manufacture of nozzles, seals, bearings and other wear-resistant parts for high wear environments.
Aerospace: Used in the manufacture of lightweight, high-strength structural components such as spacecraft shielding.
Industrial cutting tools: used as abrasive or coating material for cutting, grinding, and polishing tools.
Chemical equipment: for the manufacture of corrosion-resistant reactors, pipes, and valves.
Electronic industry: used as grinding and polishing materials in semiconductor manufacturing.
Company Profile
RBOSCHCO is a trusted global chemical material supplier & manufacturer with over 12 years experience in providing super high-quality chemicals and Nanomaterials.
The company has a professional technical department and Quality Supervision Department, a well-equipped laboratory, and equipped with advanced testing equipment and after-sales customer service center.
If you are looking for high-quality Boron Carbide Plate please feel free to contact us or click on the needed products to send an inquiry.

Payment Term
T/T, Western Union, Paypal, Credit Card etc.
Packing and Storage
The product is in powder form and should be stored in a cool, ventilated place. Avoid inhalation when using it and keep away from open flames, heat sources, etc.

Shipment Term
By air, by sea, by express, as customers request.
FAQs of Boron Carbide Plate
Question 1: How hard is a boron carbide plate?
Answer: The boron carbide plate is extremely hard, with a Mohs hardness of 9.3, second only to diamond and cubic boron nitride. This ultra-hard property makes it an ideal material for wear and impact-resistant applications and is widely used in ballistic armor and industrial wear parts.
Question 2: What are the main advantages of a boron carbide plate?
Answer: The main advantages of a boron carbide plate include high hardness and wear resistance, low density for lightweight applications, high-temperature resistance with a melting point of up to 2,450°C, excellent corrosion resistance, and high neutron absorption capability for the nuclear industry.
QUESTION 3: What is the role of boron carbide plate in the nuclear industry?
Answer: The boron carbide plate is mainly used as a neutron absorption material in the nuclear industry. Due to its high neutron absorption cross-section, it is used in the manufacture of control rods and shielding materials for nuclear reactors to effectively control nuclear reactions and ensure safety.
Question 4: What is the manufacturing process of a boron carbide plate?
Answer: Boron carbide plates are typically manufactured through either a hot press sintering or a cold press sintering process. Hot press sintering is carried out at high temperatures and pressures to obtain high-density and strength plates, while cold press sintering is suitable for complex shapes through low-temperature molding and subsequent sintering treatments.
Question 5: What is the corrosion resistance of boron carbide plates?
Answer: Boron carbide plate has excellent corrosion resistance and can resist most acids, alkalis, and chemical reagents. This property makes it widely used in chemical equipment, for example, in the manufacture of corrosion-resistant reactors, pipes, and valves.
REQUEST A QUOTE
RELATED PRODUCTS

Refractory Ceramic Substrates Silicon Nitride Plates Si3N4
BN Ceramic Chemically Stable Boron Nitride Ceramic BN Film

High Quality High Hardness Corrosion Resistant B4C Boron Carbide Tube

High Quality Precision Machined Refractory Zirconia Nozzles

Grinding Media High Purity Boron Carbide B4C Grinding Balls






