Overview of Metal Alloys
Metal alloys, a blend of metals and other elements, offer superior properties to pure metals. They have been a cornerstone of engineering and manufacturing for centuries due to their strength, flexibility, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Alloys can be customized to satisfy details demands, making them crucial in numerous applications.
Characteristics of Metal Alloys
Strength and Durability: Metal alloys often exhibit higher strength and durability than pure metals, making them suitable for load-bearing applications.
Corrosion Resistance: Adding specific elements can enhance an alloy's resistance to corrosion and extend its service life in harsh environments.
Malleability and ductility: Many alloys can be easily shaped and formed into complex geometries, essential for precision manufacturing.
Thermal Properties: Some alloys exhibit excellent thermal conductivity or resistance, making them useful in thermal management applications.
Cost-Effectiveness: Alloys can often be produced more economically than pure metals, providing a cost-effective solution for large-scale manufacturing.
Application of Metal Alloys
Automotive Industry: Metal alloys, such as steel and aluminum, are widely used in automotive components for their strength, flexibility, and lightweight properties.

Automotive Industry
Aerospace: Due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, alloys like titanium and nickel-based superalloys are crucial in aerospace applications.

Aerospace
Electrical and Electronics: Copper and its alloys are essential for wiring and conductive components in electrical and electronic systems.
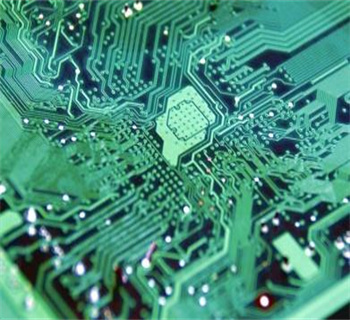
Electrical and Electronics
Jewelry and Decorative Arts: Precious metal alloys like gold and silver alloys are popular in jewelry and decorative arts for their aesthetic value and durability.

Jewelry and Decorative Arts
Medical Implants: Biocompatible alloys, such as cobalt-chromium and titanium alloys, are used in medical implants due to their compatibility with human tissue.
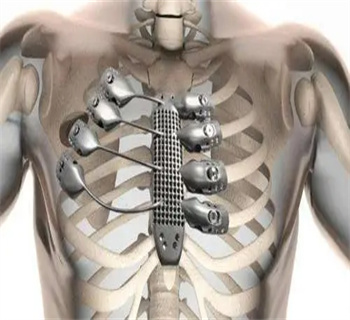
Medical Implants

Company Profile
NANOTRUN(www.rboschco.com) is a trusted global chemical material supplier & manufacturer with over 12-year-experience in providing super high-quality chemicals and nanomaterials, including boride powder, nitride powder, graphite powder, sulfide powder, 3D printing powder, etc.
The company has a professional technical department and Quality Supervision Department, a well-equipped laboratory, and equipped with advanced testing equipment and after-sales customer service center.
If you are looking for high-quality Metal alloys, please feel free to contact us or click on the needed products to send an inquiry.
Payment Term
L/C, T/T, Western Union, Paypal, Credit Card etc.

Shipment Term
By sea, by air, by express, as customers request.
FAQ
What are the most common metal alloys?
Re: The most common metal alloys include steel, brass, bronze, aluminum alloys, titanium alloys, and copper alloys. Each alloy has unique properties that make them suitable for different applications. Steel, for example, is a blend of iron and carbon, offering high strength and durability. Aluminum alloys are lightweight yet strong, making them ideal for automotive and aerospace components.
How are metal alloys formed?
Re: Metal alloys are formed by combining one or more metals with other elements, typically through melting and mixing the components. The resulting alloy has properties that are a combination of the constituent metals and elements, often superior to those of pure metals. The process can be controlled to achieve specific mechanical, physical, or chemical properties.
Are metal alloys recyclable?
Re: Yes, metal alloys are generally recyclable. Depending on the composition, they can be melted down and reprocessed into new alloys or pure metals. Recycling metal alloys reduces waste, conserves resources, and reduces energy consumption compared to producing new alloys from virgin materials.
What are the disadvantages of using metal alloys?
Re: While metal alloys offer many advantages, they also have disadvantages. One major drawback is their susceptibility to corrosion, especially in harsh environments. Additionally, some alloys may be more expensive than pure metals due to their specialized composition and production processes. Furthermore, certain alloys may not be suitable for high-temperature applications or in environments with extreme chemical exposure.
How do metal alloys affect the environment?
Re: The production and disposal of metal alloys can impact the environment. The mining and smelting processes used to produce alloys can release harmful emissions and waste. Additionally, if alloys are not recycled properly, they can end up in landfills, causing soil and water pollution. However, many industries are moving towards more sustainable production methods and recycling practices to minimize the environmental impact of metal alloys.




